Birth Control Side Effects:
Everything You Need To Know


Birth control is another name for contraception. The contraceptive pill, patch & ring are among the most used methods of birth control in Ireland – but are you aware of the side effects? We are here to help! Let’s discuss the side effects associated with taking birth control and contraception.
But Wait… What Is Birth Control?
Birth control or contraception is used as a method of preventing pregnancy. Different types of birth control are available, and they are only effective when used correctly. Take the time to learn about what birth control is, and which type is right for you.
If you’re sexually active but don’t want to get pregnant, you should look into taking birth control. Pregnancy can occur at any time when you have unprotected sex, however, birth control does not protect you from contracting an STI.
What Are the Most Common Birth Control Methods?
In Ireland, the combined contraceptive pill, patch, and ring are the most commonly used kinds of birth control.
How they work:
- Keep the ovaries from releasing an egg each month (ovulating)
- Thicken the mucus near the womb’s neck, making it more difficult for sperm to enter
- Thin the lining of the uterus, making successful implantation of a fertilised egg less likely
Let’s have a look at the side effects of the most commonly used methods of birth control in Ireland.
Different Contraceptive Pills And Their Side Effects
Combined Contraceptive Pill
The combined pill contains synthetic versions of the female hormones oestrogen and progesterone, which are naturally generated in the ovaries. The combined pill is also used to help with heavy or painful periods, PMS (premenstrual syndrome), or endometriosis.
If you are over 35, smoke, or have certain medical issues, the combination pill is not for you.
This contraceptive pill does not protect you against STIs, you should still wear a condom when having sex.
Potential Side effects:
The combined pill is generally very well tolerated but can occasionally cause side effects such as:
- Headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, and mood swings at first
If they do not go away after a few months, switching to a different pill may help - It can raise your blood pressure
- Breakthrough bleeding and spotting are frequent in the first few months of taking the pill, and
- It has been related to some long term side effect, such as:
- Thrombosis (blood clots)
- Breast cancer
- Cervical cancer
Please see below for more information on long-term side effects.
Progesterone Only Pill
The progestogen-only pill (POP) is also known as the ‘mini pill’. It contains the hormone progesterone but not oestrogen. It has fewer risk factors than the combined pill and provides excellent contraceptive cover if taken correctly. You should take the progestogen-only pill at the same time every day.
The progestogen-only pill works by thickening the mucus in the cervix, preventing sperm from reaching an egg. Depending on the type of progestogen-only pill you take, it can also prevent ovulation. (Newer pills containing desogestrel are more effective at preventing ovulation)
This contraceptive pill does not protect you against STIs, you should still wear a condom when having sex.
There are two kinds of progestogen-only pills available in Ireland. Each contains a different type of progesterone and a different time window for missed pills.
It is important to note that if you forget to take your pill at the usual time, and it is longer than the time frame for your specific pill, then it is considered a missed pill and cannot be relied upon for contraception.
Potential Side Effects:
The progestogen-only pill is generally well tolerated, and most patients do not have any significant side effects when using this. Some possible side effects include:
- Acne
- Breast tenderness/ enlargement
- Mood swings
- Increased or decreased sexual libido (sex drive)
- Headache or migraine
- Nausea or vomiting
- Cysts (small fluid-filled sacs) on your ovaries (these are normally harmless and go away on their own)
These side effects tend to occur during the first few months of taking the progestogen-only pill. They usually get better with time and should end within a couple of months.
There is a small risk of some serious side effects when you use a hormonal contraceptive such as the contraceptive pill. These include blood clots (thrombosis) and cancer.
If you have any concerns regarding your contraceptive pill, you should speak to a GP. They may advise you to try a different pill or method of contraception.
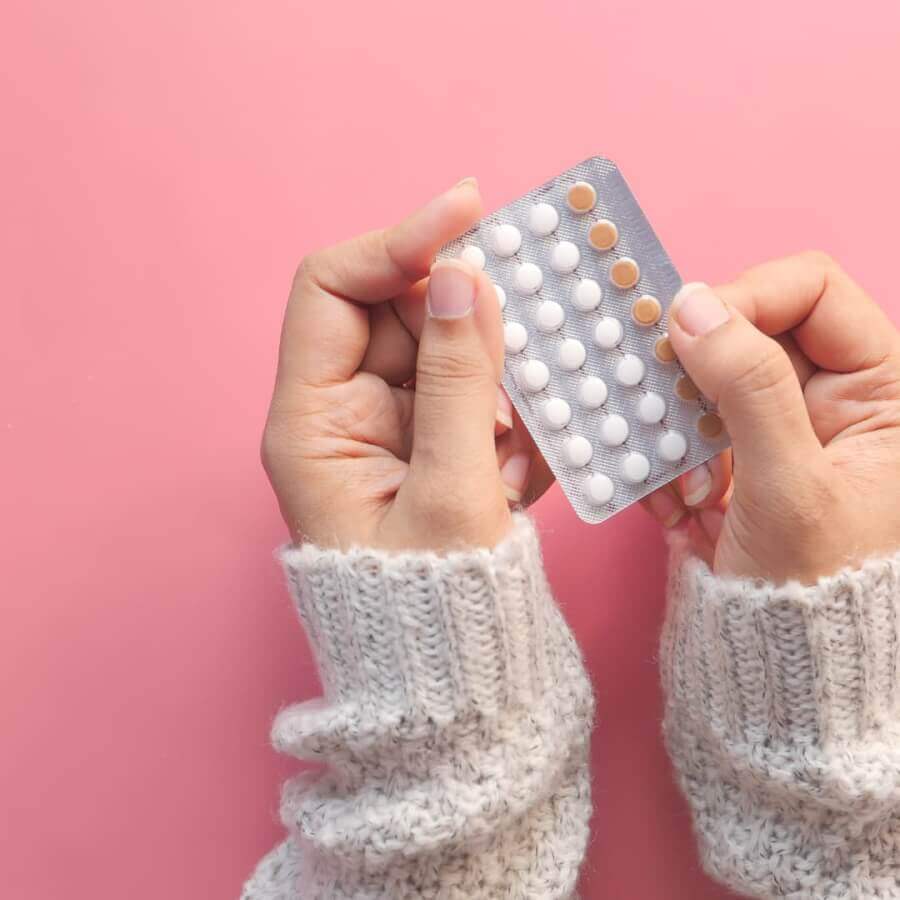

The Contraceptive Patch And Its Side Effects
The contraceptive patch is a small sticky patch that releases hormones into your body through your skin and into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy. It includes the same hormones as the combination pill – oestrogen and progestogen – and operates in the same way by thinning the lining of the womb, thickening the mucus, and preventing the release of one egg each month (ovulation).
The contraceptive patch does not protect you against STIs, you should still wear a condom when having sex.
Side effects:
When starting to use the contraceptive patch, some women may experience:
- Breast pain
- Skin irritation (at the patch site)
- Moderate headaches
- Bloating
- Breakthrough bleeding (bleeding between periods)
Although these can be bothersome, they are not dangerous and should go away after a few months of using this contraceptive. If they do not, are you are unable to tolerate any side effects, you should speak with your doctor.
There is a small risk of some serious side effects when you use a hormonal contraceptive such as the contraceptive patch. These include blood clots (thrombosis) and cancer.
The Contraceptive Ring And Its Side Effects
A vaginal ring is a small soft plastic ring that you insert into your vagina. It is placed in the vagina for 3 weeks. It releases the hormones oestrogen and progesterone hormones into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy.
The vaginal ring can also be used to alleviate premenstrual symptoms and make bleeding lighter and less painful.
The vaginal ring does not protect you against STIs, you should still wear a condom when having sex.
Side effects:
Some women have temporary side effects, including:
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
There is a small risk of some serious side effects when you use a hormonal contraceptive such as the vaginal ring. These include blood clots (thrombosis) and cancer.
For most women, the benefits of the ring outweigh the possible risks, however, you should discuss all risks and benefits with a GP before you start it.
Are There Ways To Reduce Side Effects Of Birth Control?
The best way to reduce side effects with any form of birth control is to find the right type for you. There is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to contraception, so it may take some trial and error to find the one that best agrees with you. Luckily, you can speak with a GP to discuss your options. You may be able to find a tailored regime that works for you.

Are There Any Long-Term Side Effects of Birth Control Pills?
Most women experience minor side effects when starting a new form of contraception, and usually, these are short-lived.
Long-term side effects of birth control are rare. As with any medication, there are some risks. Your medical history, as well as your age, may raise your chances of experiencing some long-term side effects. Some long-term side effects include:
- Blood clots (thrombosis)
- There is an increased risk of blood clots when taking birth control
- The risk is higher if you or your immediate family have a history of blood clots
- Highest when you start or re-start the pill for the initial 6-12 months of use (This is why starting/ stopping or taking a break from the pill without a good reason should be avoided)
- Cancer
- Birth control pills can increase your risk of some cancers
- E.g., breast cancer & cervical cancer
- They can also reduce the risk of developing other cancers
- E.g., endometrial and ovarian cancer
- Birth control pills can increase your risk of some cancers
- Fertility
- There is a common misconception that birth control can harm your fertility, particularly if it is taken for long periods of time – this is not true
- Once you stop taking birth control, it has no effect on your fertility
Birth control pills are intended to be taken for an extended period of time. You should be safe to continue taking them as long as they were recommended by your doctor and do not cause any ongoing side effects.
It’s important to remember that your body and lifestyle will change as you get older, which means your medical and contraceptive needs will likely change as well.
If you want to discuss your contraceptive needs, you can speak to a GP online now.
Repeat Prescription
Contraceptive Pill, Patch & Ring
Request a prescription for the Contraceptive Pill, Patch & Ring online with Webdoctor.ie! Once your request has been approved, we can send your prescription directly to your chosen pharmacy via secure Healthmail.
How Can I Get A Prescription For The Contraceptive Pill, Patch Or Ring?
Webdoctor.ie’s online prescription service makes it quick and easy to request a contraceptive prescription.
Simply fill out a simple and secure questionnaire to request your prescription. Once this is complete, one of our Irish-registered doctors will review your request to ensure that it is safe and suitable for you. The prescription is then sent directly to an Irish pharmacy of your choosing.
There is no need to make a GP appointment unless this is your first time obtaining a contraceptive prescription. If this is the case, you can book an online video consultation with one of our 40+ Irish-registered GPs.
How It Works
Through an online medical questionnaire, face-to-face video consultation or home health test, our online doctors will review your case and prescribe the best treatment for you.
Step 1
Online Questionnaire
Step 2
Medical Review
