The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck. Although it is small, it is mighty as it plays an important role in our overall health. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate our metabolism, which is an important part of all key bodily functions, such as body temperature and heart rate. But, what happens when the thyroid gland isn’t functioning properly? Here, we’re going to take a look at symptoms, causes and treatment options for hyperthyroidism or an “overactive thyroid”.
Overactive Thyroid Symptoms
As mentioned, the thyroid impacts core bodily functions, such as heart rate and body temperature. It does this by producing two hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyronine which are key to regulating the metabolism of every cell in the body. This means that it regulates the rate at which cells burn energy and impacts everything from how much energy you have to body weight to your cholesterol levels.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when your thyroid gland produces too much thyroxine and triiodothyronine, meaning your thyroid is overactive.
Hyperthyroidism can cause a range of different symptoms, some mimic symptoms associated with other conditions. Therefore, it can be tricky for doctors to diagnose an overactive thyroid. Some of the most common hyperthyroidism symptoms include:
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia): Typically defined as more than 100 beats per minute
- Irregular heart rate (arrhythmia)
- Pounding of the heart (palpitations)
- Increased appetite
- Nervousness, anxiety, irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Tremors in the hands and fingers
- Increased sweating
- Increased sensitivity to heat (feeling warm/ hot all the time)
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
- Changes in bowel patterns: Especially more frequent, loose bowel movements
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- An enlarged thyroid gland (also known as goiter): This may appear as a swelling at the base of the neck.
Older people may present with very mild symptoms or no symptoms at all.
Graves’ Ophthalmopathy
Grave’s ophthalmopathy is possibly one of the more well-known associations with an overactive thyroid. However, it is not common. Graves’ ophthalmopathy affects the eyes, causing the tissues and muscles behind the eyes to swell. This causes the eyes to protrude, giving a “bulging” appearance. This condition can also cause the eyes to become dry, red and swollen. You may experience excessive tearing or discomfort in your eyes. In addition, many people with this condition experience blurred or double-vision and reduce eye movement due to the inflammation.
What Causes An Overactive Thyroid?
Just like hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid), there are many potential causes. Some of the most common causes include Graves’ disease, hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules and thyroiditis.
- Graves’s disease: This is an autoimmune disease that causes antibodies produced by the immune system to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce more thyroxine. This is the most common cause of an overactive thyroid.
- Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules: Sometimes an adenoma (part of the thyroid gland that has walled itself off from the rest of the gland) grows, forming noncancerous lumps. This, in turn, causes the thyroid gland to grow larger, producing too much thyroxine.
- Thyroiditis: This occurs when the thyroid becomes inflamed and the excess thyroid hormone that is stored in the gland leaks into the bloodstream. For some people, thyroiditis can be painful. For others, it does not cause any discomfort.
Anyone can develop hyperthyroidism at any stage in their life, but some people are at higher risk. For instance, if you’re female you are more likely to develop this condition. You also have an increased chance of developing hyperthyroidism if you have a family history of thyroid disorders or Grave’s disease. Similarly, if you have a personal history of autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes, pernicious anaemia or primary adrenal insufficiency, you may be more likely to develop an overactive thyroid.
Can Hyperthyroidism Cause Other Health Problems If Left Untreated?
If you have any of the above-mentioned symptoms and suspect you could have developed hyperthyroidism, you should consult a doctor and get your thyroid function tested. If left untreated, an overactive thyroid can cause many potentially serious health conditions, such as heart problems, eye problems, and brittle bones (osteoporosis).
As thyroid hormone helps to regulate heart rate, it’s not surprising that untreated hyperthyroidism could potentially impact your heart health. An overactive thyroid can cause your heart to beat significantly faster than normal. This increases your risk of a heart rhythm disorder, including a potentially serious heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation. This disorder significantly increases your risk of stroke and congestive heart failure.
Without treatment, an overactive thyroid can also impact your bone health. We need calcium to ensure our bones stay strong and healthy. Hyperthyroidism affects the body’s ability to absorb calcium into the bones, leaving them brittle, weak and at risk of osteoporosis.
As mentioned earlier, people with Grave’s ophthalmopathy develop eye problems including eye irritation, swelling, and blurred or double-vision. If this condition is not treated, it could lead to vision loss.
How Do I Know If I Have Developed Hyperthyroidism?
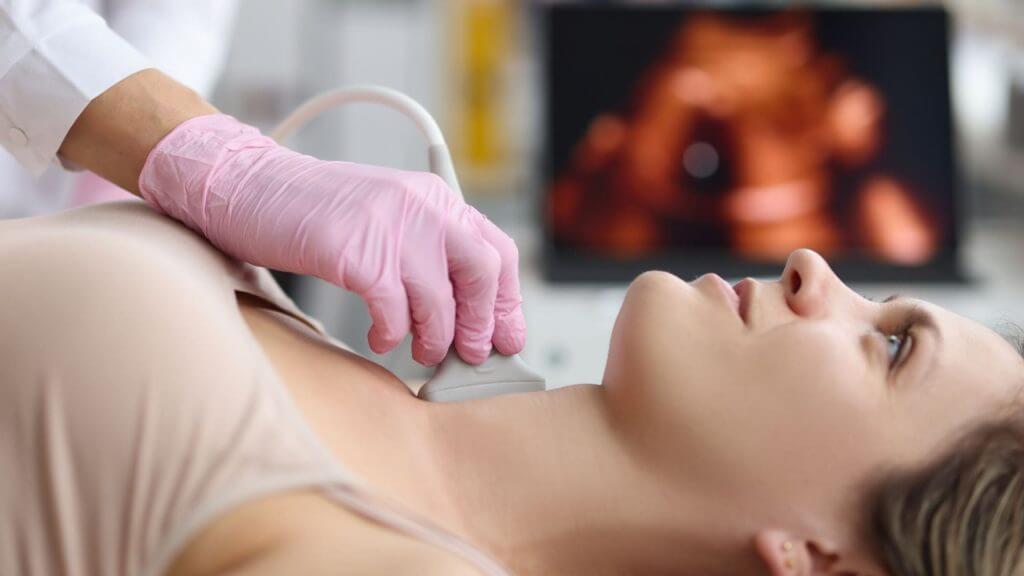
If you have symptoms and you suspect that you may have developed hyperthyroidism, there are tests that can help lead to a diagnosis. Specialists can arrange specialised thyroid scans to assess the function of your thyroid gland. Ultrasound scans can be performed to look at the structure of your thyroid gland. You can also use a simple blood test to check if your thyroid is functioning normally. For instance, Webdoctor.ie’s Thyroid Home Test Kit measures your thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) levels.
How do Webdoctor.ie Thyroid Home Test Kits work? You can order a Home Test Kit online and we will deliver it directly to your door. Don’t worry, all Home Test Kits are packaged in discreet packaging for your privacy. When your kit arrives, you simply follow the instructions to collect a small blood sample. Then, you return the kit to our accredited laboratory partner using the pre-addressed envelope. When your results are available, we will share them with you via your secure online medical file on your Webdoctor.ie account. One of our experienced, Irish Medical Council-registered doctors will also review your results so they can offer advice if any further action is needed.
There are several hyperthyroidism treatment options available. For instance, you can use anti-thyroid medication to reduce thyroid hormone production. Alternatively, you can use radioactive iodine medication to shrink the thyroid gland and therefore decrease hormone production.
You can learn more about hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) in our article, “What Is An Underactive Thyroid (Hypothyroidism)?” You can also access more medically-reviewed health and wellness content on our social media channels. Join us on Facebook, Instagram and Twitter!









